SUMMARY
What is taurine used for? It’s clear that taurine benefits the body in several ways. This amino acid supports your eyesight, and studies show that taurine supplementation may help ward off diabetes.
Fresh N’ Lean is the nation’s largest organic meal delivery service. Our tasty, chef-prepared cuisine is always fresh and never frozen, and we offer five convenient meal plans: Protein+, Keto, Paleo, Standard Vegan and Low-Carb Vegan. Choose Fresh N’ Lean for affordable nutrition, delivered to your doorstep.
There’s a fair amount of misinformation out there regarding taurine.
First of all, many people believe this nutrient is derived from bull semen or bull urine. Taurine can be found in many animal-based foods, but it’s not taken from those bull fluids.
And the fact that taurine is heavily used in energy drinks – many of which are loaded with unhealthy ingredients – may lead you to believe that it’s bad for you. However, in truth, taurine is a natural amino acid that can benefit your health.
With those basics covered, it’s time to learn all about the many ways in which taurine consumption can assist you on your health journey.
In this article, we will:
- Explain what taurine is and how it impacts the body
- Discuss how taurine is synthesized
- List some ways in which taurine benefits your health
- Share common food sources of taurine
- Offer dosage recommendations for taurine supplementation
- Discuss how taurine benefits the health of your pets
What is taurine?
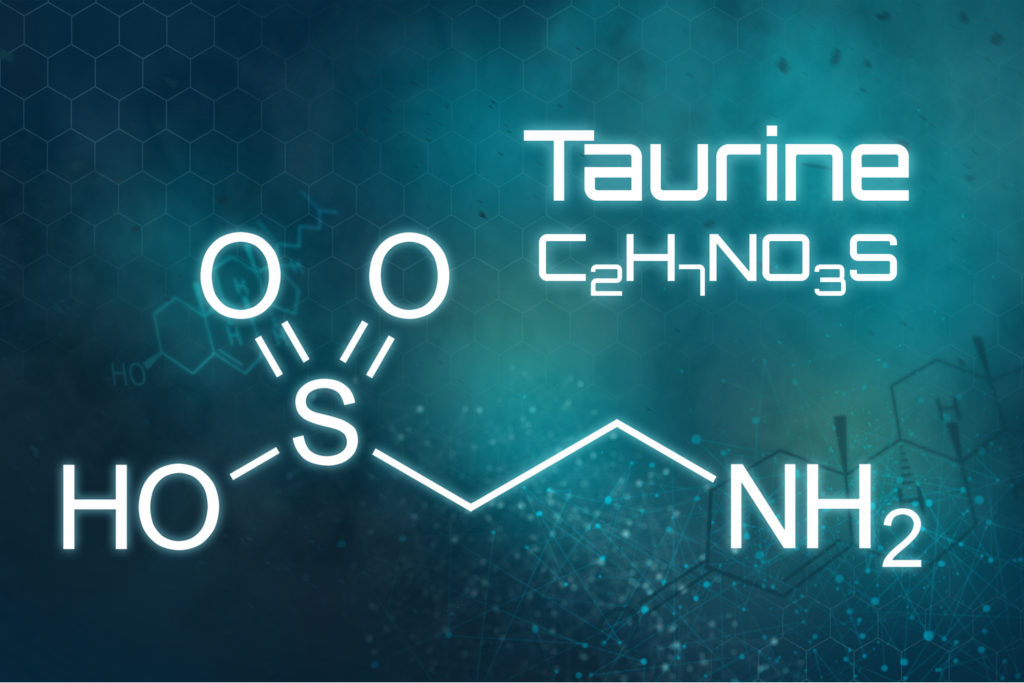
Taurine is an essential amino acid, and its chemical name is 2-aminoethanesulfonic acid. If you have any familiarity with amino acids, you know that they play a broad and vital role in health and wellness.
This is certainly true for taurine. Taurine benefits and supports your body in countless ways. For example, it helps your body form bile salts — from bile acid — that are integral to digestion. From your heart to your eyes to your central nervous system, taurine plays an essential part in helping various parts of your body function at their very best.
Origin
Taurine’s name offers a clue regarding its origin. The word taurine comes from the Latin word taurus, which means bull or ox. This amino acid got that name because it was first discovered in ox bile back in the early 1800s.
A conditionally essential amino acid
Taurine is known as a conditionally essential amino acid or conditional amino acid. As with other amino acids, it’s derived from cysteine. However, taurine lacks a carboxyl group that is usually found in amino acids. Instead of the carboxyl group, taurine contains a sulfide group. Because of this, it’s best described as an amino sulfonic acid.
Typically, the body can produce conditionally essential amino acids on its own. However, during times of sickness and stress, production may be compromised.
As with many amino acids, taurine occurs naturally in the body. It’s found in especially high amounts in the heart, eyes, brain and skeletal muscle. It’s even present in the breast milk that mothers produce to feed their babies.
What is taurine synthesis?

So, how does the body create taurine? It’s synthesized naturally in the pancreas. This takes place during what’s called the cysteine sulfinic acid pathway.
The process begins with the oxidation of the sulfhydryl group on the cysteine molecule; this leads to the formation of cysteine sulfinic acid. Next, this acid undergoes decarboxylation. This causes it to become hypotaurine, and, finally, taurine.
There are some foods that naturally contain taurine. This amino acid is typically obtained in the diet from meat and fish.
However, taurine can also be produced in the lab via chemical synthesis. To make this happen, ethylene oxide and sodium bisulfite are combined to create isethionic acid. This acid is then used to create a synthetic form of taurine. Another approach involves combining aziridine and sulfurous acid.
Synthetic taurine is commonly used in taurine supplements. This type of lab-made taurine doesn’t involve the use of animal products. As a result, a dietary supplement that contains the synthetic version of this amino acid is suitable for consumption by vegans.
Taurine benefits

Taurine benefits your health in several key ways:
1. May combat diabetes
High blood sugar is a key factor in type 2 diabetes.
Taurine is effective at keeping blood sugar within healthy levels. As such, it’s an excellent tool for fighting and preventing diabetes.
In a 2012 study, taurine supplementation decreased fasting blood sugar levels in diabetic rats. This was accomplished without any modifications to diet or exercise.
Some studies suggest that adding a taurine dietary supplement may help prevent diabetes. Researchers speculate that this benefit stems from taurine’s ability to reduce blood sugar levels and enhance insulin resistance.
It’s also worth noting that research shows people with diabetes tend to have low levels of taurine. This is another piece of evidence that supports taurine’s role in fighting diabetes.
2. May reduce the risk of heart disease
Taurine benefits heart health in significant ways.
Studies show that this amino acid can help reduce your likelihood of developing cardiovascular disease and experiencing heart failure. And researchers have established a link between higher taurine levels and lower fatality rates from heart disease.
High blood pressure can place great strain on your blood vessel walls, and this can ultimately damage your heart and cause congestive heart failure. Taurine reduces high blood pressure. It does this by minimizing the resistance to blood flow within the walls of your blood vessels. As an added plus, this amino acid also works to mute nerve impulses in your brain that can cause your blood pressure to rise.
Inflammation and artery thickening are causative factors in heart disease and heart failure. Taurine benefits the heart by curbing inflammation, and it can help reduce thickening of the arteries. As such, taurine supplementation is a good idea if you’re interested in protecting the heart muscle and fostering heart health.
3. May improve exercise endurance and athletic performance

Endurance is important if we want to reap maximum benefit from our workouts. We have to hang in there long enough to burn fat and build muscle.
Taurine benefits your workouts by supporting endurance. Studies show that this amino acid can improve muscle performance. In research done with rats, taurine mitigated muscle damage and fatigue during exercise
As waste products build up in our bodies, they can cause fatigue and muscle burn. Human studies show that taurine helps remove waste products from the body. In so doing, taurine can help reduce fatigue and muscle soreness as we complete our workouts.
For the reasons discussed above, taurine also enhances athletic performance. Studies show that runners who supplement with taurine are able to cover longer distances with less fatigue.
4. Supports healthy weight loss
Roughly 70 percent of Americans are overweight or obese. That means weight loss is key issue for many people.
One health benefit of taurine is that it helps speed up fat burning during exercise. It makes your body more likely to use fat for fuel when you work out. In so doing, taurine benefits your fitness by supporting healthy weight loss.
In a 2010 study involving cyclists, taurine supplementation increased fat burning by 16 percent.
5. Supports eye health

There is a large amount of taurine present in your retina. A diminished retinal taurine level has been linked with vision problems. The good news is that this kind of taurine deficiency can be easily reversed via supplementation.
Taurine deficiency has also been linked with certain retinal diseases. Retinal ganglion cell (RGC) degradation is a condition that occurs in numerous diseases that harm the retina, and it can ultimately lead to blindness.
Research shows that taurine benefits the eyes by preventing this type of retinal degeneration. As such, taurine consumption may play a role in warding off eye disease and protecting your vision.
6. Supports gum health
Periodontal disease is more common that you might realize. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), 47 percent of American adults who are 30 and older have some form of gum disease. And the risk increases with age. It’s estimated that gum disease affects 70 percent of adults who are 65 and older.
Taurine is an effective antioxidant. It’s able to reduce oxidative stress in the gums and blood. In so doing, it can improve oral health and help treat gum disease.
In a 2014 study that looked at people with gum disease, those treated with taurine showed a statistical improvement in the health of their gums.
7. Supports your hearing
What is taurine capable of doing for your hearing? Studies show that this amino acid can help revive the health of nerve cells in your ears. In so doing, taurine may be able to help you optimize your hearing.
Ringing in the ears – also known as tinnitus — is a symptom that’s associated with hearing loss, and it’s a condition that affects many Americans. In one study involving people who suffer from tinnitus, taurine supplementation completely eliminated this condition in 12 percent of participants.
8. May protect against brain aging and neurodegenerative diseases
As mentioned, taurine is present in the brain. But the amount decreases as we age, and this can have negative implications for cognition and brain function.
It makes sense, then, that supplemental taurine can have a positive effect on the way the brain works.
In one study, taurine supplementation was shown to promote healthy long-term memory storage. Scientists also believe that taurine may be able to reduce the likelihood of developing neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s.
A 2014 study looked at the effect that taurine had on mice with Alzheimer’s. The study showed that taurine supplementation helped reduce cognitive impairment in those that have this disease.
Taurine food sources

Taurine is mainly found in meat, fish and dairy. As such, vegans and vegetarians are especially prone to taurine deficiency. People in these groups can benefit tremendously from taurine supplementation.
Here are some taurine food sources:
- Tilapia
- Clams
- Shrimp
- Tuna
- Cod
- Salmon
- Scallops
- Turkey
- Octopus
- Chicken
- Nori
- Beef
Taurine dosage

Taurine supplements typically contain between 500-1,000 milligrams per serving. It’s common for people to take between 500 and 2,000 milligrams of this supplement per day. Research shows that it’s safe to supplement with up to 3,000 milligrams of taurine daily for an entire lifetime.
This amino acid supplement is available in pill form or as a powder.
What is taurine used for in pet health?

Taurine isn’t just good for humans. Research shows that taurine benefits the health of your pets in significant ways.
Some veterinarians recommend a taurine supplement for dogs or taurine for cats as a treatment for dilated cardiomyopathy.
Some pet foods are fortified with this nutrient. For example, taurine-enriched cat food is available, it it can help provide the nourishment needed to keep your feline’s heart and eyes in good health.
Next steps
What is taurine doing for your health? Now that you know all about the ways in which taurine benefits your wellness, give some serious thought to adding this supplement to your daily routine. Taurine supplements are available online or in health food stores.
Support your health journey by making nourishing foods a part of your diet. You can easily access these foods by subscribing to Fresh N’ Lean. Our meal plans range from vegan to keto; some options include taurine-rich foods such as salmon and cod. For your convenience, our organic, chef-prepared cuisine is delivered straight to your door.




