SUMMARY
Vitamin D deficiency can have a huge impact on your health, and it’s been linked with everything from rickets to cardiovascular disease. The signs of D deficiency include depression, joint pain and eczema.
Fresh N’ Lean is the nation’s largest organic meal delivery service. Our tasty, chef-prepared cuisine is always fresh and never frozen, and we offer five convenient meal plans: Protein+, Keto, Paleo, Standard Vegan and Low-Carb Vegan. Choose Fresh N’ Lean for affordable nutrition, delivered to your doorstep.
It’s a fact: Vitamin D deficiency can have consequences that negatively impact your health, your mental state and your productivity.
For example, if you’re noticing more hair loss than usual, vitamin D deficiency may be to blame. And if you’re struggling with depression or fatigue, low vitamin D levels may play a role. Also, your vitamin D status may affect your likelihood of developing conditions such as cardiovascular disease.
This deficiency can prevent you from feeling your best, looking your best and optimizing your productivity. It may very well be the one thing that’s preventing your from living a more fulfilled life.
A vitamin D deficiency is relatively easy to address. But the first step lies with identifying the problem, and that requires knowledge and awareness.
Most recently, vitamin D has been in the news for its effect on those with COVID-19. Research shows that D deficiency may play a role in the severity of COVID-19 symptoms.
These facts mean there are some compelling reasons for learning more about D deficiency and supplementation.
In this article, we will:
- Explain what vitamin D is, and talk about the role it plays in the body
- Let you know which groups have the highest risk of vitamin D deficiency
- Discuss the relationship between COVID-19 and vitamin D
- Explain the signs that indicate you may have a low vitamin D level
- List some illnesses linked to vitamin D deficiency
- Discuss your options for vitamin D supplementation
- Let you know which foods are rich with vitamin D
- Explain how much vitamin D you should get each day
- Share recipes for dishes that contain this nutrient
Vitamin D basics

Vitamin D is also referred to as calciferol. This fat-soluble vitamin is found in certain foods. Your body can generate vitamin D if you give your skin sun exposure. And vitamin D supplements are available that can ramp up your stores of this vital nutrient.
Your gut needs vitamin D to help it absorb calcium. And your body needs calcium to produce strong, healthy bones.
Without enough vitamin D, bones can become weak and misshaped. In children, this condition is called nutritional rickets; in adults it’s called osteomalacia. If there is vitamin D insufficiency in older adults, it can lead to osteoporosis.
Here are some ways in which vitamin D supports your body:
- This nutrient plays a key role in helping the body reduce inflammation, a condition that’s been linked with a wide range of chronic diseases.
- Vitamin D plays an essential role in cell growth all over the body.
- Genes that encode proteins regulating cell differentiation and apoptosis are partially modulated by vitamin D.
- The immune system relies on vitamin D as it works to protect the body from harmful bacteria.
- Your muscles need this nutrient to operate smoothly; if there is vitamin D insufficiency, you may experience muscle cramps, as well as muscle weakness, spasms and contractions.
Vitamin D deficiency is rampant; it’s more widespread than most people realize. According to an estimate published in Oxford Journals Age and Aging, more than 1 billion people have vitamin D deficiency or insufficiency worldwide. And some groups of people are more likely to have low vitamin D levels than others.
Which people have the highest risk of vitamin D deficiency?

These groups of people have the highest risk of vitamin D deficiency and inadequacy:
1. Older adults
During sunlight exposure, the skin initiates the process of creating vitamin D. This process tends to grow less efficient as we mature in years. Because of this, older people have a more difficult time creating vitamin D from sunlight than younger people do.
2. People with limited sun exposure
You need to be outside in the sun with part of your skin exposed to produce vitamin D. Because of this, people who fall into the categories listed below are at higher-than-normal risk of D deficiency due to their limited sun exposure:
- Homebound people. People who are homebound don’t spend time outdoors, so they have less opportunity to create this vitamin.
- Those whose jobs force them to spend most of their time indoors. Certain jobs require you to spend lots of time indoors. If this is true of your job, the lack of sunlight exposure could hinder your body’s ability to make enough vitamin D.
- Those who keep most of their bodies covered for religious reasons. For religious reasons, some people wear long robes, dresses or head coverings. These garments block the skin from the sun. Because of this, they can prevent the body from producing healthy levels of vitamin D.
- People who always wear sunscreen. Sunscreen shields the skin from the sun’s rays, and in so doing, it can diminish vitamin D production. Keep in mind, though, that sunscreen plays a vital role: It can help prevent skin cancer.
3. People with dark skin
Melanin affects the body’s ability to produce vitamin D. The more melanin you have in your skin, the more likely it is that you will suffer from low vitamin D levels.
This is clearly reflected in the data. According to the National Institutes of Health (NIH), non-Hispanic blacks are more likely than other groups to have insufficient vitamin D. Among all groups, non-Hispanic whites tend to have the highest vitamin D level.
4. People who have difficulty digesting fat
Since vitamin D is fat soluble, it needs fat if it is to be properly processed by the body. Certain diseases make fat digestion difficult.
These medical conditions may hinder fat digestion:
- Certain forms of liver disease
- Cystic fibrosis
- Celiac disease
- Crohn’s disease
- Ulcerative colitis
If you suffer from any of these conditions, you may have a higher-than-normal risk of vitamin D insufficiency.
5. Obese people
Body fat can sometimes prevent vitamin D from being properly absorbed into the bloodstream. Obese people have high levels of body fat. This could ultimately hinder efficient vitamin D absorption and leave them deficient.
6. People who have had gastric bypass surgery
Gastric bypass surgery is also known as bariatric surgery, and it’s used to treat obesity. In this operation, part of the upper small intestine is removed to help facilitate weight loss.
The section of the intestine that is excised helps produce vitamin D in the gut. As a result, if you’ve had a gastric bypass, you’ll likely have to take special care to make sure you’re getting enough vitamin D.
What’s the relationship between COVID-19 and vitamin D?

COVID-19 is a virus that can affect the respiratory system. It’s a new disease, and lot of research is still being done to learn more about this condition. But it’s undeniably deadly; it’s already resulted in more than 300,000 fatalities in the United States alone.
Research indicates there may be a link between vitamin D status and the severity of COVID-19 symptoms. Some studies show that as many as 80 percent of those who have been hospitalized with COVID-19 have low vitamin D levels.
Researchers are still in the early stages of figuring out how vitamin D can help those with COVID-19. But one Spanish study looked at 76 patients who have been hospitalized with COVID-19 symptoms. Fifty of these patients received vitamin D. Of this group, none died, and only one required treatment in the intensive care unit (ICU). The remaining 26 patients did not receive vitamin D. Of this bunch, 13 needed ICU treatment and two died.
What are signs of vitamin D deficiency and insufficiency?

These signs may indicate vitamin D deficiency or insufficiency:
1. Frequent respiratory infections
Vitamin D keeps your immune system robust and ready for battle. In so doing, it helps you fight off common respiratory infections such as colds and the flu.
If you frequently get ill from respiratory infections, it’s possible that your immune system may not be getting the vitamin D it needs to wage war on harmful viruses.
A number of studies have shown that there is a link between vitamin D levels and the likelihood of developing respiratory tract infections. Data indicates that those with low levels of vitamin D are more likely to develop respiratory infections that are more frequent and more severe.
2. Constant fatigue

Constant fatigue can be caused by many different factors. One common causal factor is vitamin D insufficiency.
Research indicates that if vitamin D levels are inadequate, it can cause tiredness that severely impacts your productivity and overall quality of life. In some cases, the resolution can be dramatic and relatively quick once vitamin D supplementation is introduced.
In one such case, a 61-year-old man was experiencing excessive daytime fatigue. He was examined for common causes such as depression, sleep apnea and narcolepsy, but none of these appeared to be a factor. Tests revealed he had low vitamin D levels, and supplementation was initiated. After taking a vitamin D supplement for just three months, the patient reported a complete resolution of his daytime fatigue.
3. Back pain
Back pain is a common affliction. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), one study showed that as many as 25 percent of American adults reported lower back pain the prior three months. Opioids are commonly prescribed to address this condition, even though there is an overall lack of evidence to support the efficacy of this course of treatment.
Several studies have established a relationship between vitamin D deficiency and chronic lower back pain. One study looked at the link between vitamin D levels and back pain in roughly 9,300 older women. The research showed that participants with low levels of vitamin D were more likely to have back pain. This includes severe back pain that limits mobility and hinders a person’s ability to carry out basic daily tasks.
4. Bone and joint pain
We’ve mentioned that vitamin D helps keep your bones healthy and strong. If your body doesn’t have enough of this nutrient, you could wind up experiencing pain in your bones and joints.
Research shows there’s a link between a low vitamin D level and bone pain. A 2010 study involving 276 participants established a connection between skeletal pain and vitamin D deficiency. Participants with insufficient levels of this vitamin were nearly twice as likely to experience pain in the bones and joints than those whose levels were in the normal range.
5. Slow wound healing
Your body relies on vitamin D to assist in the generation of new cells. It’s not surprising, then, that low levels of this vitamin have been linked to slow wound healing.
In a 2016 study, vitamin D was found to play a crucial role in the formation of new skin. And in a 2011 study, gum surgery patients with vitamin D deficiency experienced poorer outcomes with regards to wound healing following their procedure.
6. Depression

According to CDC estimates, 4.7 percent of adults 18 and over suffer from regular feelings of depression. And according to the World Health Organization, depression affects 264 million people across the globe. Worldwide, it’s a leading cause of disability, and it can result in suicide. Roughly 800,000 deaths each year are caused by suicide.
Research indicates there’s a link between major depression and lower-than-normal levels of vitamin D. In one study, vitamin D supplementation was used to successfully treat depression.
7. Hair loss
There are many different causes of hair loss. Vitamin D inadequacy plays a role in at least two of these causes:
- Alopecia areata is an autoimmune disease that can leave you with coin-sized bald patches on your scalp. Research has established a link between this disease and vitamin D deficiency. A 2014 study showed there is a significant correlation between alopecia areata and low vitamin D levels.
- Vitamin D inadequacy also plays a role in female pattern hair loss. In a 2013 study, this type of hair loss was more likely to be experienced by women with low levels of vitamin D.
8. Bone loss
As we mentioned earlier, vitamin D inadequacy has been linked with bone and joint pain. Low vitamin D levels can impact the bones in another ways, as well: This condition has been associated with bone loss.
Many people think low bone mineral density is caused by insufficient calcium. Calcium inadequacy can certainly play a role, but vitamin D insufficiency is also a causal factor in this condition.
The research backs this up. In a 2015 study involving 1,106 women between the ages of 45 and 65, findings established a strong link between low bone mineral density and D deficiency.
9. Muscle pain

Muscle pain can be caused by many different things. Research shows that in some cases, D deficiency may be a causative factor.
A 2014 study looked at 174 patients with chronic pain. The study determined that 71 percent of participants who had chronic pain were deficient in vitamin D.
10. PMS
PMS is an abbreviation that stands for pre-menstrual syndrome. This term is used to describe symptoms that some women get a week or two prior to their period. According to the Mayo Clinic, as many as 75 percent of all menstruating women have experienced PMS.
The symptoms include:
- Tender breasts
- Food cravings
- Mood swings
- Fatigue
- Depression
- Irritability
Research has shown there’s a link between D deficiency and PMS symptoms. A 2005 study determined that women with a low level of vitamin D were more likely to develop PMS.
11. Eczema
Eczema is a condition that can cause skin to become red and inflamed. Research shows that D deficiency may play a role in causing this disease.
A 2011 study looked at children with atopic dermatitis, a type of eczema. According to the study, symptom severity was linked with vitamin D levels; participants with the most severe symptoms had the lowest levels of vitamin D.
In another study, vitamin D supplementation helped relieve eczema in afflicted children.
12. Gum disease
Research has shown there’s a link between gum disease and factors such as diet and smoking. The latest evidence shows that D deficiency may also increase of person’s likelihood of developing this disease.
Illnesses linked to vitamin D deficiency

Vitamin D deficiency is a risk factor in these illnesses and conditions:
- Rickets
- Diabetes
- Cognitive impairment
- Heart disease
- Breast cancer
- Peripheral vascular disease
- Stroke
- Hypertension
- Multiple sclerosis
What vitamin D supplements are available?
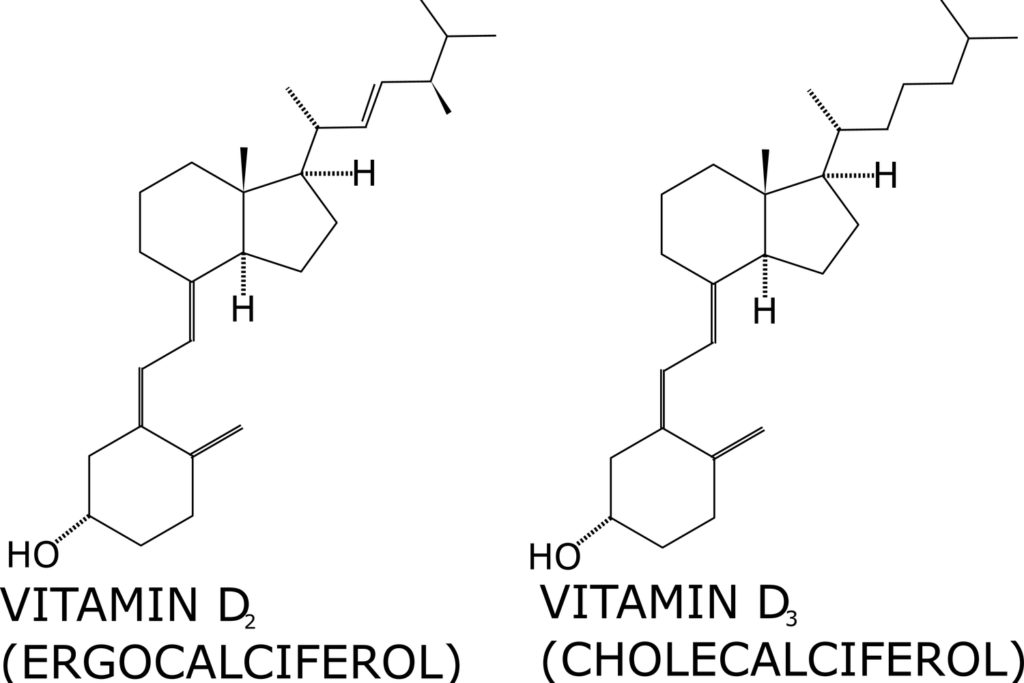
There are two types of vitamin D supplement on the market: vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol) and vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol).
They differ in source of origin. Vitamin D3 is animal-based, while D2 is plant-based.
Typically, vitamin D2 is made by exposing yeast to ultraviolent light. Vitamin D3 can be extracted from fish. It can also be obtained by exposing the lanolin found in sheep’s wool to ultraviolet light.
Which foods contain vitamin D?
Some foods are natural sources of vitamin D. Others are fortified with this nutrient to make them more nourishing.
Natural food sources

There aren’t too many foods that are naturally abundant in vitamin D. You’ll find this nutrient in these menu items:
- Fatty fish and other seafood. Oily fish such as salmon, tuna and mackerel are good sources of vitamin D, and they’re also rich in vital omega-3 fatty acids. Additionally, you’ll find vitamin D in shrimp and oysters.
- Beef liver. Are you a fan of beef liver? If so, know that it contains some vitamin D.
- Cheese. Cheese is an addictive treat. This food can supply you with small amounts of vitamin D.
- Eggs. Eggs can help boost your vitamin D intake. More specifically, this nutrient is found in the yolk.
- Mushrooms. Most vitamin D food sources are animal-based, but there’s one that’s plant-based: mushrooms. Some are specifically cultivated in ways that boost their vitamin D levels. This is accomplished by exposing them to ultraviolet light.
Fortified food sources
To help fight vitamin D insufficiency, many foods are fortified with this valuable nutrient:
- Dairy milk. Most of the cow’s milk sold in the United Stated is fortified with vitamin D. However, know that the same isn’t true of dairy products. That means foods such as ice cream don’t have added vitamin D.
- Plant-based milks. Plant-based milks have been riding a wave of popularity with consumers over the past few years. The list of choices includes soy milk, oat milk and almond milk. Many people are lactose-intolerant, and plant-based milk gives them an alternative to dairy milk that’s easier to digest. As with cow’s milk, plant-based milks are typically fortified with vitamin D.
- Orange juice. Orange juice is a morning staple for many. This juice typically contains added vitamin D. This isn’t the case with all orange juice on the market, so check the label for vitamin D content before buying.
- Breakfast cereals. Some breakfast cereals up their nutritional content by adding vitamin D.
How much vitamin D should you get each day?

The amount of your recommended vitamin D intake will depend on your age. NIH provides these recommendations:
- 0-12 months: 400 IU
- 1-13 years: 600 IU
- 14-18 years: 600 IU
- 19-50 years: 600 IU
- 51-70 years: 600 IU
- Over 70 years: 800 IU
Recipes to increase your vitamin D levels

These recipes contain nourishing vitamin D:
Speedy Salmon Patties
This dish pairs canned salmon with eggs for a tasty treat. And it takes just 25 minutes to make.
Shrimp ‘n Noodle Bowl
Combining angel hair pasta with cooked shrimp, this dish is a pleasure for the senses. Prep/cooking time is just 25 minutes.
Egg-Topped Avocado Toast
Avocado toast is a trendy favorite with foodies. This version adds eggs, cheese and butter for added protein and vitamin D. It takes 20 minutes to prepare.
Cod with Sweet Peppers
This dish includes cod fillets, green pepper and garlic cloves. It’s comfort food that’s good for you, and it contains health-supporting vitamin D. From start to finish, it takes 25 minutes to prepare.
Next steps
Now that you know all about the signs of vitamin D deficiency, it’s time to make an assessment: Do you exhibit any of the symptoms we’ve discussed? If you suspect that your levels of this nutrient are low, schedule a visit with a doctor to determine your vitamin D status. A medical professional can conduct a test and let you know if your levels are insufficient or deficient.
If you want a quick and easy way to access foods that contain vitamin D, subscribe to Fresh N’ Lean. We offer five different meal plans that range from vegan to keto. Many of our dishes include foods that contain vitamin D, such as cod and salmon. We deliver our organic, chef-prepared meals straight to your door.




