SUMMARY
It’s impossible to overstate the importance of omega-3 fatty acids. Omega-3 benefits your health; this nutritious fat can help ward off heart disease and inflammation. You can up your intake of this nutrient by eating more omega-3 foods. These include plant-based options such as flax seeds, as well as fatty fish such as mackerel and tuna.
Fresh N’ Lean is the nation’s largest organic meal delivery service. Our tasty, chef-prepared cuisine is always fresh and never frozen, and we offer five convenient meal plans: Protein+, Keto, Paleo, Standard Vegan and Low-Carb Vegan. Choose Fresh N’ Lean for affordable nutrition, delivered to your doorstep.
If you want great health, you have to make sure your body gets the right mix of nutrients.
That mix of nutrients must include omega-3 fatty acids if you want optimum wellness. Your body needs these healthy fats to fight inflammation. They also play a role in helping to prevent heart disease.
You can get the omega-3s your body needs via a dietary supplement. A fish oil supplement will do the trick, and there are also vegan supplements that provide this vital nutrient.
Another way to access these nourishing fats is via omega-3 foods. Certain foods are high in omega-3 fatty acids.
Let’s take a closer look at omega-3 fatty acids and the delicious, nutritious foods that contain this nutrient.
In this article, we will:
- Explain what omega-3 fatty acids are, and discuss the ways in which they support the body
- Share insight regarding various omega-3 benefits as they relate to your health
- Discuss recommendations regarding daily omega-3 intake
- Provide a list of plant-based and animal-based omega-3 foods
What are omega-3 fatty acids?

Omega-3s are fatty acids that the body needs to function in good health.
Let’s talk about fatty acids for a moment. These fats may be either essential or nonessential.
The body can synthesize most of the fatty acids it needs from the food that we eat. Fatty acids that fall within this category are known as nonessential. Since nonessential fatty acids can be produced by the body, it’s not necessary for us to obtain them via our diet.
Essential fatty acids are different. The body can’t create these healthy fats on its own, so we have to get them from the foods we eat or the dietary supplements we take.
Omega-3s are classed as essential fatty acids. That means the body can’t make them, and we have to obtain these nutrients from omega-3 foods or an omega-3 dietary supplement.
You’ll find omega-3s in the membranes that surround every cell in your body. They support your heart, your blood vessels, your lungs and your immune system. They also provide vital support to your endocrine system. The endocrine system is a network of glands that produce your body’s hormones.
Types of omega-3 fatty acids

There are three main types of omega-3 fatty acids:
- Alpha-linolenic acid (ALA)
- Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA)
- Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA)
ALA comes largely from plant oils. Here are examples of plant oils that contain ALA:
- Flaxseed oil
- Soybean oil
- Canola oil
What about EPA and DHA? These omega-3 fatty acids are mainly found in fish and other types of seafood. You can find them in oily fish such as mackerel and tuna. When it comes to vegan sources of these nutrients, EPA and DHA are contained in seaweed and algae.
Certain parts of your body have high levels of DHA. These include the brain, the retina and sperm cells.
Omega-3 benefits

You can choose between omega-3 foods or supplements. Making sure you get enough omega-3 benefits your well-being in these ways:
1. Supports heart health
Heart disease is a killer. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), this condition is the leading cause of death here in the United States. In this country, one person dies of cardiovascular disease every 36 seconds.
Research shows there are notable omega-3 benefits when it comes to coronary heart disease and heart health. Studies indicate that omega-3s can help reduce your risk of getting heart disease. And research shows that omega-3 fatty acids can help keep your arteries free of the plaque that can cause serious heart problems.
2. Fights chronic inflammation
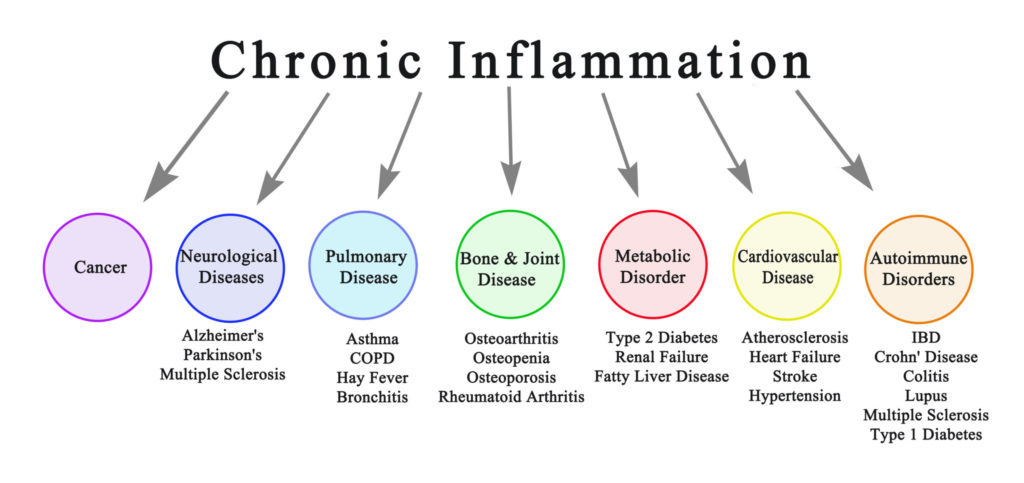
Chronic inflammation has been associated with a wide range of health problems. This condition can sap your immune system and lead to illnesses such as cancer and heart disease.
Omega-3 fatty acids provide powerful support in this area. Studies show that omega-3s work hard to help reduce inflammation in the body.
3. Fights age-related mental decline
Unfortunately, many people experience a decline in brain function as they age.
Research indicates that omega-3 foods and supplements can help support brain health in aging people. Studies show that omega-3 benefits mental functioning in older people and can help ward off cognitive decline.
4. Helps prevent cancer

Cancer is widespread in this nation, and its impact is devastating. According to the National Cancer Institute, roughly 39.5 percent of adults in this country will get a cancer diagnosis at some point in their lives
Omega-3 foods can help prevent certain types of cancer. Studies show increased intake of foods high in omega-3 may help reduce the risk of colon cancer. Research also shows that high omega-3 intake can help reduce the risk of breast cancer.
5. Supports eye health
We’ve mentioned that DHA — a form of omega-3 — is found in large quantities in the retina. With this in mind, it makes sense that omega-3 benefits eye health.
Studies show that if you don’t get enough DHA, you may develop vision problems. The research shows that these problems can be alleviated with DHA supplementation.
Then there’s the issue of macular degeneration. This condition is widespread, and it can cause blindness and permanent eye damage. Studies show that those with low intake of omega-3 foods are at higher risk for macular degeneration.
How much omega-3 do you need each day?
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) recommends that men get 1600 mg of ALA per day. For women, the figure is 1300 mg.
NIH hasn’t established recommendations regarding EPA and DHA. However, various expert sources recommend a minimum of 250-500 mg in combined EPA and DHA each day for healthy adults.
One caveat for vegans: There are lots of plant foods that contain AHA, so it’s possible to meet your recommended daily intake of this nutrient solely by including these foods in your diet. However, the situation is different with EPA and DPA; its much harder to get EPA and DHA from dietary sources if you eat only plant-based foods. For this reason, it may be a good idea to supplement with a vegan source of EPA and DHA (such as oil derived from algae) if your eating plan is exclusively plant-based.
Keep in mind that if you want to treat or address specific conditions, your omega-3 needs may be higher.
Omega-3 foods

Ready to check out a list of foods high in omega-3? Here are 61 choices (26 plant foods and 35 foods derived from animals) to consider adding to your diet:
Plant-based omega-3 foods

- Flaxseed oil – 7269 mg in 1 tbsp
- Flax seed – 6479 mg in 1 oz
- Chia seed – 5064 mg in 1 oz
- Hemp seed – 2641 mg in 1 oz
- Walnuts – 2579 mg in 1 oz
- Butternuts (dried) – 2476 mg in 1 oz
- Firm tofu – 1467 mg in 1 cup
- Walnut oil – 1414 mg in 1 tbsp
- Canola oil – 1279 mg in 1 tbsp
- Boiled soybeans (edamame) – 1029 mg in 1 cup
- Soybean oil – 923 mg in 1 tbsp
- Cod liver oil – 888 mg in 1 tsp
- Sauteed green peppers – 886 mg in 1 cup
- Mustard oil – 826 mg in 1 tbsp
- Red bell peppers (cooked) – 822 mg in 1 cup
- Soybean lecithin – 698 mg in 1 tbsp
- Mungo beans (cooked) – 603 mg in 1 cup
- Kale (cooked) – 482 mg in 1 cup
- Navy beans – 322 mg in 1 cup
- Kidney beans – 301 mg in 1 cup
- Pecans – 280 mg in 1 oz
- Chinese broccoli – 271 mg in 100g
- Brussels sprouts (cooked) – 270 mg in 1 cup
- Avocados – 255 mg in 1 cup
- Cauliflower (cooked) – 207 mg in 1 cup
- Broccoli (cooked) – 186 mg in 1 cup
Animal-based omega-3 foods

- Salmon oil – 5038 mg in 1 tbsp
- Salmon (cooked) – 4252 mg in 6-oz fillet
- Pacific herring (cooked) – 3835 mg in 1 fillet
- Sardine oil – 3508 mg in 1 tbsp
- Atlantic herring – 3373 mg in 1 fillet
- Bluefin tuna (cooked) – 2914 mg in 6-oz fillet
- Coho salmon (cooked) – 2375 mg in 6-oz fillet
- Atlantic mackerel (cooked) – 2225 mg in 1 fillet
- Sablefish (cooked) – 1827 mg in 3 oz
- Herring oil – 1823 mg in 1 tbsp
- Trout (cooked) – 1742 in 1 fillet
- Sockeye salmon (cooked) – 1727 in 6-oz fillet
- Sardines (canned) – 1649 mg in 1 cup
- Whitefish (cooked) – 1602 mg in 3 oz
- Eastern oysters (canned) – 1591 mg in 1 can
- Tilefish (cooked) – 1572 mg in ½ fillet
- Pacific oysters (cooked) – 1346 mg in 3 oz
- Anchovies (raw) – 1303 mg in 3 oz
- Striped bass (cooked) – 1199 mg in 1 fillet
- Swordfish (cooked) – 913 mg in 3 oz
- Cod liver oil – 888 mg in 1 tsp
- Fish roe (cooked) – 888 mg in 1 oz
- Pompano (cooked) – 869 mg in 1 fillet
- Smelt (cooked) – 802 mg in 3 oz
- Shrimp (canned) – 778 mg in 1 cup
- Blue mussels (cooked) – 762 mg in 3 oz
- Alaskan king crab – 615 mg in 1 leg
- Snapper (cooked) – 583 mg in 1 fillet
- Walleye pike (cooked) – 554 mg in 1 fillet
- Grouper (cooked) – 535 mg in 1 fillet
- Calamari (fried) – 470 mg in 3 oz
- King mackerel (cooked) – 457 mg in 3 oz
- Eel (cooked) – 452 mg in 1 fillet
- Spiny lobster (cooked) – 451 mg in 3 oz
- Tilapia (cooked) 408 mg in 6-oz fillet
Next steps
Now that you know all about omega-3 fatty acids, stop by your local grocery store so you can add more omega-3 foods to your pantry.
If you want to include more omega-3 foods in your diet but would rather skip the cooking and grocery shopping, subscribe to Fresh N’ Lean. Our meals are made with healthy foods high in omega-3s, and we deliver straight to your front door. Our chef-prepared meal plans range from paleo to keto.



