SUMMARY
Protein is an essential amino acid used to upkeep and improve our health. When trying to eat better, supplementing your diet with high protein foods gives your body the tools it needs to lose weight, build muscle, and more.
If you’ve started looking into eating better, or perhaps adopting a more rigorous gym routine, you’ve no doubt also seen a guide to a high-protein diet. Find out if a high protein diet is right for you, and how you can use it to meet your health goals.
For extra help on getting started with your high protein diet, try our Protein+ plan. We craft high protein meals for you, making your meal planning weeks a little easier!
Table of Contents
What is Protein?
Benefits of a High Protein Diet
Risks of a High Protein Diet
High (Healthy) Protein Food List
How Much Protein Should You Eat?
FAQs
What is Protein?
Proteins are a type of amino acid that our body uses to do all sorts of amazing things. Amino acids are long chains of molecules that twist and fold into different shapes that allow them to perform those amazing things.
Despite popular belief, protein is much more than the “building block” for muscles. Protein is involved in many biological functions including basic cell activity. This can mean acting as enzymes, signaling molecules, or even acting as antibodies that fight infection.
One example of proteins being more than muscle is tryptophan, which is actually a protein molecule that famously leads to sleepiness when consumed (like when you eat turkey at Thanksgiving). That’s quite the opposite effect you’d expect from a molecule that is just supposed to help you get big and strong!
Benefits of a High Protein Diet
Eating more protein (in regulated amounts) can offer all kinds of health benefits. Protein plays a role in repairing and maintaining tissues in muscle, skin, bone, and hair. It also aids in oxygenation of the body. These alone are starring benefits that do wonders for your health, but protein does so much more.
Protein’s Starring Role in Fitness
It is true that proteins are critical components for muscles, and that in order to build muscle you need to up your protein intake, which is what makes proteins appear to be a potent exercise and fitness tool. Higher protein intake is associated with larger muscle mass and strength when combined with the right exercises.
High protein diets can also boost your ability to heal and reduce the amount of muscle strength and bone mass you lose as you age. All around, high protein diets can make you a healthier person, especially if you’re very active.

High Protein Diets Help with Weight Loss
High protein weight loss strategies can be found everywhere since the launch of the Atkin’s diet. Nearly all of these are low carb – high protein diets can cloud the issue of whether high protein content matters for weight loss. In fact, carbohydrates tend to get most of the “credit” (check out our keto diet discussion for more info). The truth may be that it’s the high protein content in these diets that promotes weight loss, and that the carbohydrate content is irrelevant!
As always with studies on weight loss, research varies on the effectiveness of how effective high protein diets are with weight loss. However, there is a general agreement that it is a candidate to be an effective option.

High protein intake is effective even when carbohydrate content is ignored
One simple fact underlies all weight loss strategies: You must consume fewer calories than you burn in order to lose weight. All strategies attempt to address one side or the other of that equation.
Strategies that help us to feel fuller after eating are critical to reducing calorie intake – trying to not eat when you feel hungry is not sustainable for most people. High protein meals are the most filling, with protein being the most satiating, carbohydrates are second, and fat last.
So, if your meals have high protein content, you can eat fewer calories and still feel full. At the end of the day this leads to decreased total calorie intake and weight loss.
Protein Helps Burn Calories

Referencing the critical “consume fewer calories than you burn,” the “burn” side is important too – you must consider something known as “Dietary Induced Thermogenesis.” This term basically refers to the calories your body burns in order to process what you eat: every process in your body burns calories, even eating! Digestion, absorption, transport, and storage all require energy.
Increasing Metabolic Rate to Burn More Calories
Proteins have by far the highest Dietary Induced Thermogenesis effect because your body burns far more calories to process proteins than carbohydrates or fat.
One study compared the metabolic rate of subjects eating a high protein (29%) diet vs. not (11%) and found that the high protein subjects burned an additional 891 calories per day!
This is particularly critical in dieting, because when we eat less our body responds by decreasing our metabolic rate, aka the rate at which we burn calories when we are just sitting still, the calories burned by our normal cellular processes
This can adversely affect the balance between calories consumed and calories burned (if you consume less AND burn less, then you won’t lose weight). By selectively consuming protein we can maintain a high metabolic rate despite dieting.
Boosts Physical Ability and Stamina

Exercise is the best way to burn a lot of calories – you burn a lot while in the gym, and you also dramatically raise your metabolic rate by increasing the amount of muscle mass in your body. And, of course, consuming protein is critical to aiding muscle growth when you exercise
High protein diets also can help you maintain your muscles as you lose weight. Normally with a calorie deficit your body would shed pounds in the form of muscles as well as fat. High protein diets can limit this.
SUMMARY
High protein diets contribute to greater muscle and bone mass, better athletic performance, stamina, and general better health. A higher protein diet can also contribute to better weight loss and metabolism speed.
Risks of a High Protein Diet
In combination with bad press that carbohydrates and fat are the enemy, this has led to an appreciation that high protein foods are more health-forward than other options. While it is true that high protein foods can be more health-forward, it is not quite that straightforward.
It is important to note that (as with anything) too much protein can be harmful for your body. High protein foods are often loaded with unhealthy components that more than offset any benefits they may have had. In general, high protein diets are quite safe, but there are a couple of things to keep in mind.
Puts a Strain on Your Kidneys
Your kidneys are responsible for detoxifying your blood stream. When you consume excess amino acids, your body can only utilize or store a certain amount. The rest is excess and needs to be dealt with. This job falls partially to your kidneys, which must work overtime in order to handle it when your protein consumption gets extreme.
Studies on this subject have been mixed, with some suggesting a direct relationship between protein consumption going up and long-term kidney function going down, while others showing either no relationship or there only being risk for people whose kidneys are already damaged and therefore unable to handle the extra work.

Suffice it to say, your kidneys are important, and this is not a risk to be taken lightly. If you plan on following a high protein diet, be sure to involve your doctor in the decision so they can monitor your kidney function. Losing weight is critical to your health and, if a high protein diet will help you lose weight, it is well worth the risk if you are carefully monitoring along with your doctor!
It’s also worth mentioning that chronic kidney disease is very common, and many people looking to lose weight are already at high risk for kidney problems (diseases like hypertension, diabetes, and obesity all put major strain on the kidney). It is very important to work closely alongside your primary care doctor to watch out for these issues.
SUMMARY
Because your body can only use and store so much protein, eating too much of it can damage your kidneys, who are responsible for processing and filtering things like amino acids in your blood.
Where You Get Your Protein
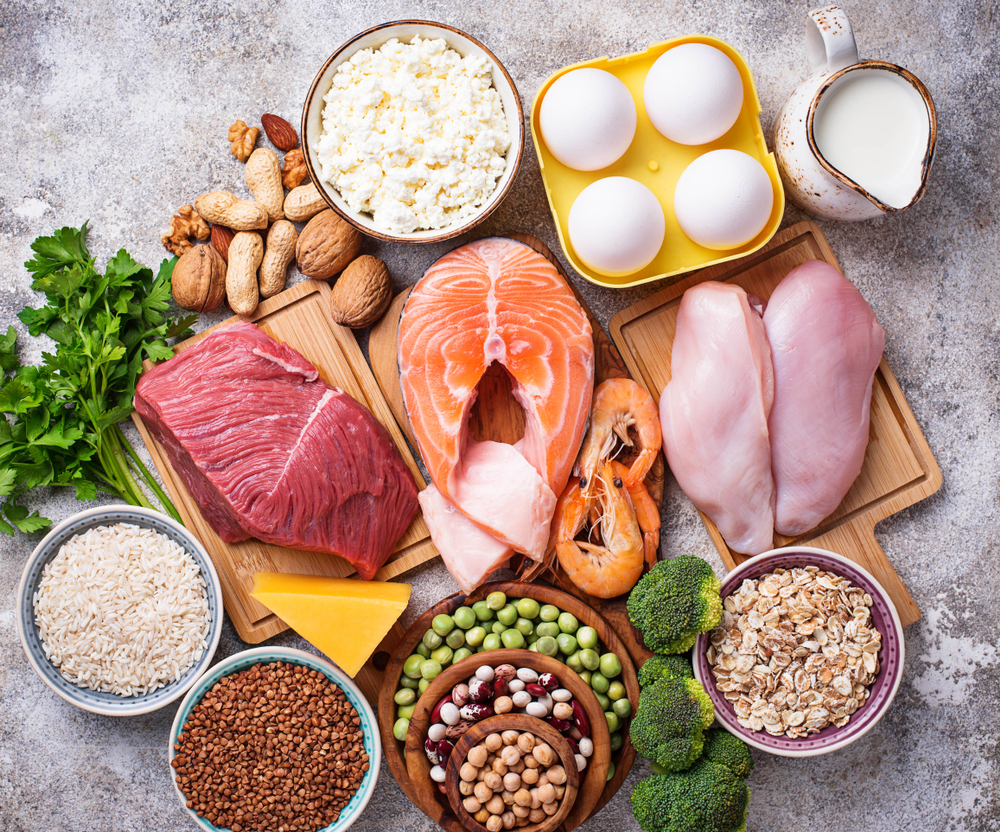

When pursuing a high protein diet, it is important to consider your protein source in order to protect your health. Many foods that are high in proteins are also high in saturated fats and cholesterol which are concerning. This is a common criticism of the keto diet (and Atkins once upon a time before it) that people lose weight but eat a huge amount of red meat and dairy products making the diet dangerous long term.
High levels of these ingredients put dieters at risk of heart disease and high cholesterol. It is possible to maintain a high protein diet without compromising your diet in other ways, but it requires carefully selecting your protein sources.
So where should you get your protein from?
High (Healthy) Protein Food List
When thinking of high protein diets, many might think of a meat-heavy diet. Fatty red meat and high-fat dairy are not great to eat on a regular basis, however. Both have high saturated fat and, though high in protein, will likely lead to health problems if consumed too often.
Lean red meat is occasionally okay, as the overall content of fat is low even if much of that fat is saturated, though one should still limit consumption of this if possible. Low fat dairy is a good, healthy option. Dairy has many health benefits and, without the saturated fat, can be perfectly healthy.
Here’s a brief list of high protein foods perfect for a healthy diet. For a more extensive list, check out our 10 Healthiest High Protein Foods blog.
Vegetarian & Vegan Protein Options
There is an association between high protein diets and eating lots of land-animal meat. While true that meat is high in protein, it is entirely possible to eat a high protein diet that’s vegetarian!
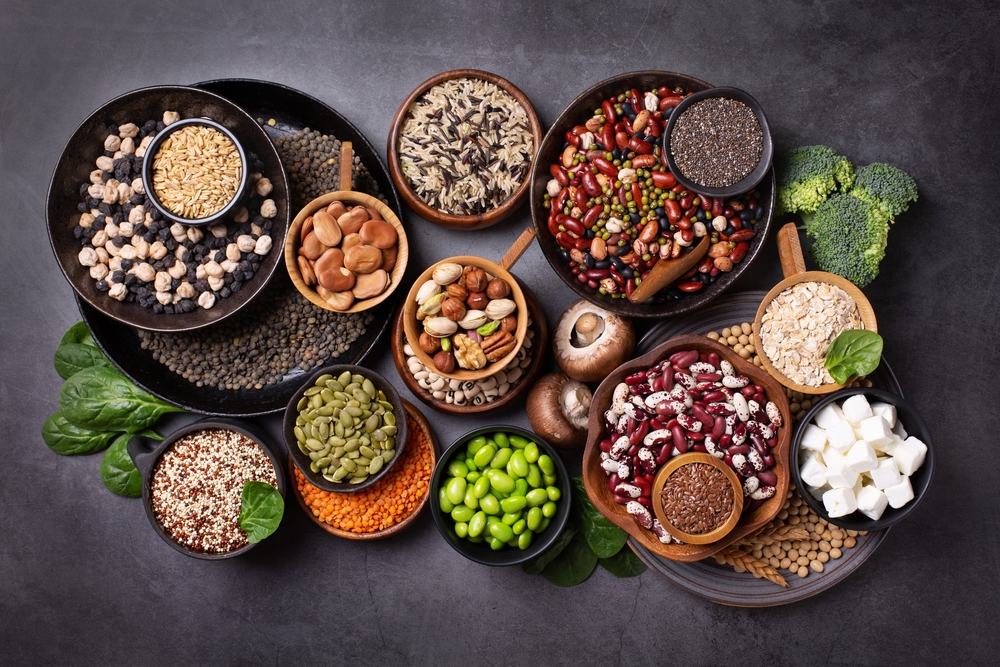

Not only that, but vegetarian diets are extremely healthy. They are low in saturated fat, low in cholesterol, high in fiber, and highly nutritious. Vegetarians tend to be thinner, have lower cholesterol, lower blood pressure, and less heart disease.
Soy (Tofu and Edamame)
▪ 1 cup of tofu contains 20g of protein, vs. 35g for chicken
▪ 1 cup of edamame contains 18g of protein
▪ Both are low calorie but extremely filling due to the combination of high fiber / high protein and have many other health benefits, too
Lentils
▪ 18g protein per cooked cup
▪ Also high in fiber
Beans
▪ 15g protein per cooked cup
▪ Very high in fiber
▪ Unlike red meat which leads to high cholesterol and heart disease, beans have been shown to lower cholesterol and prevent heart disease
Quinoa & Other Ancient Grains
▪ Quinoa has 8g of protein in a cooked cup
▪ Many of these “carb” choices are high in protein
▪ You could eat a serving of quinoa with tofu and nearly match the protein found in a chicken breast
Nuts & Seeds
▪ Most nuts and seeds have at least a moderate amount of protein
▪ Almonds have 7g protein per ¼ cup, which is about a handful
▪ Flax seeds have 3.5g of protein in just one tablespoon. (They also contain omega-3 fatty acids which are critical nutrients that you may be missing if you don’t eat fish twice per week)
▪ Nuts and seeds are also highly nutritious and packed with antioxidants
Dairy Protein Products

Eggs
▪ One egg has 7g of protein and only 50-75 calories!
▪ Eggs do have high fat content, including a lot of cholesterol, but many studies suggest they are healthy nonetheless
▪ Studies suggest that eating an egg every day does not cause heart disease, and may in fact lower your risk of cardiovascular disease
Low/No Fat Dairy
▪ One 6oz container of non-fat plain yogurt has 10g of protein
▪ Nonfat cottage cheese has 13g protein/serving
▪ One slice of low-fat Swiss cheese has 8g of protein
▪ The fat in dairy is primarily the “bad” kind (saturated fat), so consuming fatty dairy like whole milk or regular cheese is detrimental to your health
▪ With the saturated fat removed, dairy becomes a recommended part of any healthy diet and an excellent source of protein
Animal/Meat Protein Products

Fish
▪ Fish provides many important nutrients and is a critical source of omega-3 fatty acids
▪ Salmon contains 37g of protein in one 6oz serving
▪ Tuna, meanwhile, has even more protein with 48g in a 6oz filet! Even a can of tuna (5oz) contains 20g of protein
▪ Eating fish at least twice per week is considered integral to a healthy diet, and should certainly be part of any high-protein meal plan
Chicken
▪ Chicken breast has 31g protein in a 165-calorie serving (about the size of one breast)
▪ One skinless thigh (about 200 calories) has 28g of protein
▪ Chicken breasts are healthier than chicken thighs due to the lower fat content
Red Meat
▪ Red meat is best limited or avoided due to major health concerns associated with it
▪ However, it is possible to offset this by eating only lean red meat (eye of round or flank steak from beef, or pork tenderloin)
SUMMARY
Foods rich in protein include lean red meats, chicken, fatty fish, low fat dairy, and plant sources like soy, lentils, and quinoa.
How Much Protein Should You Eat?
Normal recommended dietary allowances of protein are around 0.8g/kg of body weight. Anything higher than that is considered high protein, and you may want to ease into higher protein content in your diet.
Studies on high protein diets for weight loss are generally utilizing between 1-1.6g protein/kg of bodyweight, or around 30-35% of your total daily calories from protein.

Calculating your macro percentages is probably the best way to create a high protein diet that helps you lose weight, and there are resources on the internet to help with this. But to start more simply, just aim for around 1g/kg and move up as needed to match your weight loss goals.
Whether your goal is to lose weight, get big and strong, or both, consuming a high protein diet is key. Remember, dietary changes are supposed to last a lifetime! So, you do not have to do it all at once.
FAQs
What is a High Protein Diet?
A high protein diet is full of healthy foods that exceed the basic daily allowance for protein intake as outlined by the FDA. (About 0.36 grams per pound of your body weight)
Benefits of a High Protein Diet
Eating a high protein diet can lead to increased muscle mass, controlled appetite, an increase in metabolic rate, weight loss, and general positive effects for body composition, aging, and healing.
How Much Protein Do You Need?
The amount may vary, but usually you would calculate your daily recommended protein intake by eating more than your daily recommended intake (DRI): 0.8g / kg of body weight. Or, if you track your “macros”, that would be 10-35% of your daily calorie intake coming from protein.
For example, a 150lb person would eat about 82-110g of protein daily to achieve a high protein diet.
Is a High Protein Diet for Me?
If you’re thinking about starting a new diet, it’s always a good idea to talk it over with your doctor.
In general, a high protein diet is beneficial for most, unless you have serious kidney issues.
What Are the Pros and Cons of a High Protein Diet?
High protein foods are associated with weight loss and higher physical performance, but too much protein can lead to kidney disease, cholesterol problems, heart disease, and nutrition deficiencies in other areas.
Animal Protein vs Plant Protein
Although lean meats, eggs, and chicken are high in protein, they aren’t the only way to load up on a high protein diet. Many vegetarian and vegan options like soy products, lentils, beans, quinoa, nuts, and seeds are essential and healthy sources for protein.
Can You Lose Weight Eating High Protein?
Absolutely! However, this is usually achievable with proper balance between the rest of your diet, and exercise.
Is a High Protein, Low Fat Diet Effective for Weight Loss?
Yes, especially because many high protein foods like red meats can be high in “bad” fats, which is not ideal (or good) for healthy weight loss.
What Foods Are the Highest in Protein?
Vegetables: Edamame, lentils
Grains: Quinoa, ancient grains
Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, flaxseed
Dairy: Eggs, plain yogurt, low-fat cottage cheese, low-fat Swiss cheese
Meat: Salmon, white meat chicken, skinless chicken thigh, tuna, round or flank beef steak, pork tenderloin
Other: Tofu and other soybean products
Can You Eat Too Much Protein?
You can eat too much of a good thing. Too much protein can flood your kidneys with excess amino acids it needs to filter out. This can put a strain on your system and cause long-term kidney function issues.
What Does a High Protein Diet Do to Your Body?
Eating a high protein diet can boost your body’s ability to build and repair muscle, organ, and bone tissues, lower body fat, help you feel fuller/more satiated, and reduce muscle loss as you age.



